Welcome to the realm of mole to mole ratio worksheet answers, where stoichiometry takes center stage! In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of mole to mole ratios, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to tackle these problems with confidence.
Whether you’re a student grappling with the basics or an experienced chemist seeking to refresh your understanding, this resource has got you covered.
Delve into the fundamental concepts of mole to mole ratios, their significance in stoichiometric calculations, and practical applications in chemistry. Master the steps involved in solving mole to mole ratio problems, avoiding common pitfalls, and harnessing this powerful tool to determine limiting reactants, calculate reaction yields, and explore advanced concepts like empirical and molecular formulas.
Mole to Mole Ratio Worksheet Basics
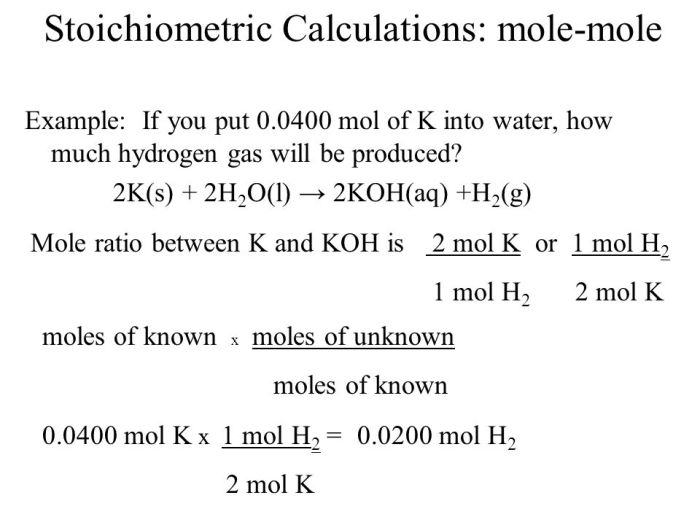
A mole to mole ratio is a relationship between the number of moles of two or more substances involved in a chemical reaction. It is used to convert between the quantities of reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation.
Mole to mole ratios are important in stoichiometry, the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions.
To determine the mole to mole ratio, we use the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation. For example, in the reaction 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O, the mole to mole ratio of hydrogen (H2) to oxygen (O2) is 2:1, and the mole to mole ratio of hydrogen (H2) to water (H2O) is 2:2.
Solving Mole to Mole Ratio Problems
To solve mole to mole ratio problems, follow these steps:
- Balance the chemical equation.
- Identify the mole to mole ratio from the coefficients in the balanced equation.
- Convert the given quantity of one substance to moles using its molar mass.
- Use the mole to mole ratio to convert the moles of the given substance to the moles of the desired substance.
- Convert the moles of the desired substance to its mass or volume using its molar mass or molar volume.
Applications of Mole to Mole Ratio
Mole to mole ratio has various applications in chemistry, including:
- Determining limiting reactants
- Calculating reaction yields
- Predicting the products of a reaction
- Balancing chemical equations
- Determining the composition of unknown compounds
Advanced Mole to Mole Ratio Concepts, Mole to mole ratio worksheet answers
Advanced mole to mole ratio concepts include:
- Empirical and molecular formulas
- Determining the composition of unknown compounds
- Relationship between mole to mole ratio and chemical equations
Frequently Asked Questions: Mole To Mole Ratio Worksheet Answers
What is the significance of mole to mole ratios in stoichiometry?
Mole to mole ratios provide a quantitative understanding of the relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions, allowing for accurate predictions of reaction outcomes.
How do I determine the limiting reactant in a reaction using mole to mole ratios?
Compare the moles of each reactant to their respective stoichiometric coefficients. The reactant with the lowest mole-to-coefficient ratio is the limiting reactant.
What are some common errors to avoid when solving mole to mole ratio problems?
Ensure proper unit conversions, pay attention to significant figures, and double-check your calculations to minimize errors.