Suppose that a monopolistically competitive restaurant, a business operating within a market structure characterized by numerous sellers offering differentiated products, enters the scene. This analysis delves into the intricacies of such an establishment, examining its pricing strategies, product differentiation, advertising tactics, and the dynamics of entry and exit within the industry.
Monopolistic competition, a hybrid market structure, blends elements of both perfect competition and monopoly, creating a unique and intriguing business environment for restaurants. This exploration unveils the complexities of this market structure, providing valuable insights into the decision-making processes and competitive landscape faced by monopolistically competitive restaurants.
Restaurant Market Structure
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which there are many buyers and sellers, and each firm produces a differentiated product. This means that each firm’s product is unique in some way, and consumers have a preference for one firm’s product over another.
As a result, each firm has some market power, but it is limited by the presence of other firms.
Some examples of monopolistically competitive restaurants include:
- Fast food restaurants
- Casual dining restaurants
- Fine dining restaurants
Pricing and Output: Suppose That A Monopolistically Competitive Restaurant
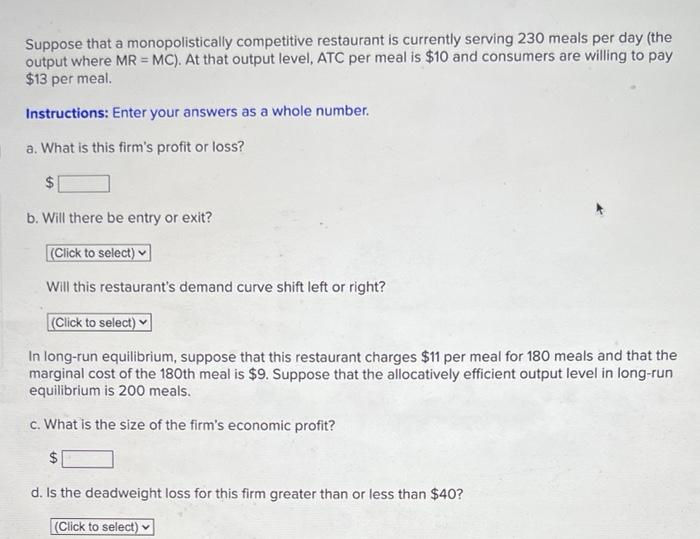
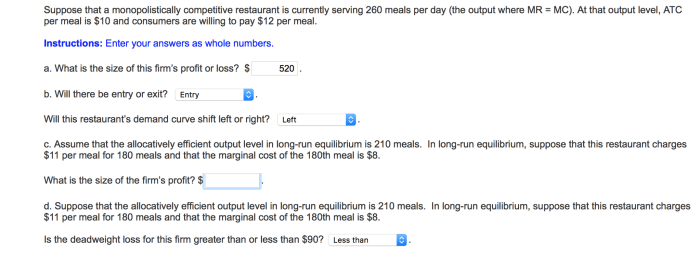
A monopolistically competitive restaurant determines its price and output by maximizing its profits. The profit-maximizing price is the price at which the marginal revenue from selling one more unit of output is equal to the marginal cost of producing that unit.
The following table compares the price, output, and profits of a monopolistically competitive restaurant to a perfectly competitive restaurant:
| Monopolistically Competitive Restaurant | Perfectly Competitive Restaurant | |
|---|---|---|
| Price | > Marginal cost | = Marginal cost |
| Output | < Output at which marginal revenue = marginal cost | Output at which marginal revenue = marginal cost |
| Profits | > 0 | = 0 |
Product Differentiation
A monopolistically competitive restaurant can differentiate its products in a number of ways, including:
- Product quality:The restaurant can offer high-quality ingredients, well-prepared dishes, and a comfortable dining experience.
- Service:The restaurant can provide friendly and attentive service.
- Atmosphere:The restaurant can create a unique atmosphere, such as a romantic setting or a lively bar scene.
- Location:The restaurant can be located in a convenient or desirable location.
Some examples of product differentiation in the restaurant industry include:
- McDonald’s:McDonald’s offers low-priced, fast food in a convenient location.
- Olive Garden:Olive Garden offers Italian-American food in a family-friendly atmosphere.
- The Cheesecake Factory:The Cheesecake Factory offers a wide variety of dishes in a casual dining setting.
Advertising and Promotion

Advertising and promotion play an important role in monopolistic competition. Restaurants use advertising to create awareness of their products and to persuade consumers to choose their restaurant over others. Restaurants use a variety of advertising and promotion techniques, including:
- Television commercials
- Radio commercials
- Print advertising
- Online advertising
- Social media marketing
- Coupons and discounts
Entry and Exit
The conditions for entry and exit in a monopolistically competitive market are relatively easy. This is because the products are differentiated, so new firms can enter the market without having to compete directly with existing firms. Similarly, firms can exit the market without having to worry about losing all of their customers to other firms.
However, there are some barriers to entry and exit in the restaurant industry. These barriers include:
- Capital requirements:Opening a restaurant can be expensive, so new firms may have difficulty raising the necessary capital.
- Location:The location of a restaurant is important, so new firms may have difficulty finding a suitable location.
- Competition:The restaurant industry is competitive, so new firms may have difficulty competing with existing firms.
Common Queries
What is the key characteristic of a monopolistically competitive restaurant?
A monopolistically competitive restaurant operates in a market where numerous sellers offer differentiated products, allowing for some degree of market power but facing competition from similar establishments.
How does a monopolistically competitive restaurant determine its price?
Monopolistically competitive restaurants consider both the demand for their differentiated product and the actions of their competitors when setting prices, aiming to maximize profits.
What role does advertising play in monopolistic competition?
Advertising is crucial in monopolistic competition, as it allows restaurants to differentiate their products, create brand awareness, and influence consumer preferences.