How does the gasb recommend governments report budgetary information – GASB’s budgetary reporting standards provide a comprehensive framework for governments to disclose financial information in a transparent and consistent manner. These standards aim to enhance the accountability and effectiveness of public sector financial management.
The GASB standards encompass various aspects of budgetary reporting, including the types of information to be disclosed, the formats to be used, and the timeframes for reporting. By adhering to these standards, governments can improve the quality and accessibility of budgetary information, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions.
GASB Reporting Standards: How Does The Gasb Recommend Governments Report Budgetary Information
The Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB) is an independent, private-sector organization that establishes accounting and financial reporting standards for state and local governments in the United States. GASB’s mission is to develop and issue high-quality accounting and financial reporting standards that are clear, concise, and understandable, and that promote transparency, accountability, and sound financial management.
GASB’s reporting standards for budgetary information are designed to ensure that governments provide transparent and reliable information about their financial plans and performance. These standards are based on the following key principles:
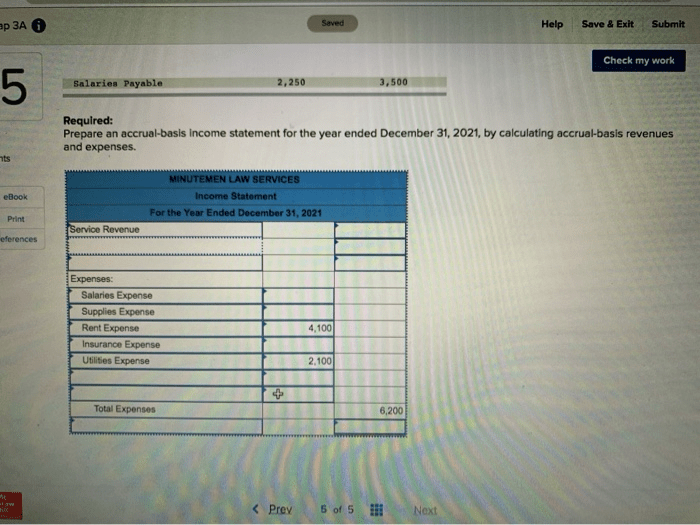
- Materiality:Only information that is material to the understanding of the government’s financial position and performance should be reported.
- Relevance:The information reported should be relevant to the needs of users, including taxpayers, creditors, and policymakers.
- Reliability:The information reported should be accurate and verifiable.
- Comparability:The information reported should be comparable to information reported by other governments, both within the same jurisdiction and across jurisdictions.
Budgetary Information Disclosure
GASB’s reporting standards require governments to report the following types of budgetary information:
- The budget:The budget is a financial plan that Artikels the government’s expected revenues and expenditures for a specific period of time, typically one year. The budget should include information on the government’s operating budget, capital budget, and debt service budget.
- Budgetary amendments:Budgetary amendments are changes to the budget that are made after the budget has been adopted. Amendments may be made to increase or decrease revenues or expenditures, or to transfer funds between different budget categories.
- Actual revenues and expenditures:Actual revenues and expenditures are the actual amounts of money that the government has received and spent during a specific period of time. Actual revenues and expenditures should be compared to the budget to assess the government’s financial performance.
- Budgetary variances:Budgetary variances are the differences between the budget and actual revenues and expenditures. Variances can be positive or negative, and they can be used to identify areas where the government’s financial performance is deviating from expectations.
The rationale for these disclosure requirements is to provide users with the information they need to understand the government’s financial plans and performance. This information can be used to make informed decisions about the government’s policies and priorities.
Budgetary Reporting Formats

There are a variety of different budgetary reporting formats that governments can use. Some of the most common formats include:
- Line-item budgets:Line-item budgets list revenues and expenditures by specific object or category. For example, a line-item budget might include categories for salaries, benefits, supplies, and equipment.
- Program budgets:Program budgets group revenues and expenditures by program or activity. For example, a program budget might include programs for education, public safety, and health and human services.
- Performance budgets:Performance budgets link revenues and expenditures to specific performance measures. For example, a performance budget might include measures for student achievement, crime rates, and the number of people receiving social services.
The advantages and disadvantages of different reporting formats vary depending on the specific needs of the government and its users. Line-item budgets are relatively simple to prepare and understand, but they can be difficult to use to track performance. Program budgets are more complex to prepare and understand, but they can be more useful for tracking performance.
Performance budgets are the most complex to prepare and understand, but they can provide the most information about the government’s performance.
Budgetary Reporting Timeframes

GASB recommends that governments report budgetary information on a quarterly basis. This timeframe allows users to track the government’s financial performance on a regular basis and to identify any trends or problems early on. Quarterly reporting also helps to ensure that the government’s budget is being implemented as intended.
Timely and accurate budgetary reporting is essential for ensuring that the government is transparent and accountable to its citizens. Quarterly reporting helps to ensure that users have the information they need to make informed decisions about the government’s policies and priorities.
Budgetary Reporting in Practice
Many governments have successfully implemented GASB’s budgetary reporting standards. For example, the City of Philadelphia has implemented a performance budget that links revenues and expenditures to specific performance measures. The City of Philadelphia’s performance budget has been praised for its transparency and accountability, and it has helped the city to improve its financial performance.
Another example of a government that has successfully implemented GASB’s budgetary reporting standards is the State of California. The State of California has implemented a line-item budget that is easy to understand and track. The State of California’s line-item budget has helped the state to improve its financial management and to make more informed decisions about its policies and priorities.
Common Queries
What are the key principles underlying GASB’s budgetary reporting standards?
GASB’s budgetary reporting standards are based on principles of materiality, timeliness, accuracy, comparability, and transparency.
What types of budgetary information are governments required to report under GASB standards?
Governments are required to report information on their revenues, expenditures, assets, liabilities, and net position, as well as other relevant financial data.
What are the advantages of using standardized budgetary reporting formats?
Standardized formats enhance comparability, consistency, and the ease of understanding of budgetary information across different governments.