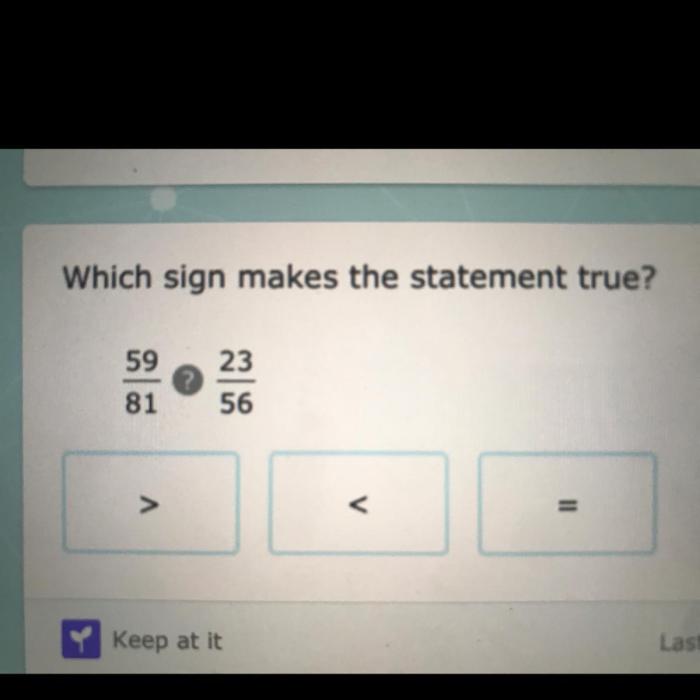
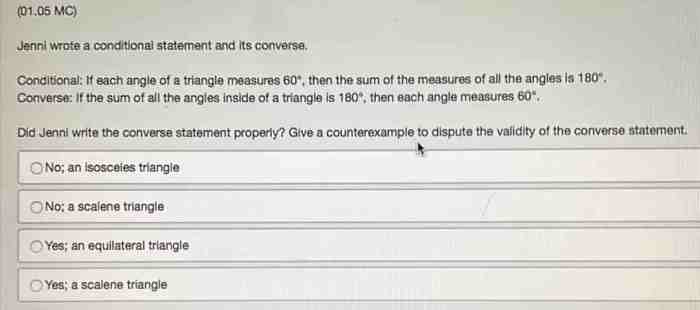
Which statement is true about the angles? Embark on a captivating intellectual odyssey that unravels the enigmatic realm of angles, their intricate relationships, and their indispensable role in shaping our world. From the fundamental concept of angular measurement to the profound applications in architecture, engineering, and navigation, this discourse promises an illuminating journey into the fascinating world of angles.
As we delve into the depths of this discourse, we will meticulously examine the diverse types of angles, unravel the intricate properties that govern their interactions, and master the art of measuring angles with precision. Through a comprehensive analysis of angle relationships in triangles, parallelograms, and circles, we will uncover the hidden symmetries and patterns that orchestrate the geometric landscape.
1. Definition of Angles
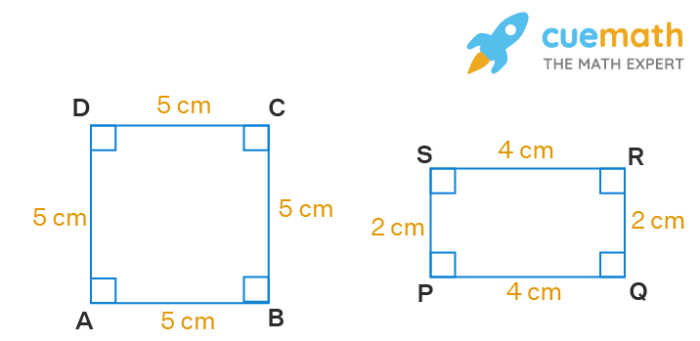
Angles are geometric figures formed by two rays that share a common endpoint, called the vertex. They are measured in degrees, with a full rotation being 360 degrees. Angles can be classified into various types based on their measure:
- Acute angles: Less than 90 degrees
- Right angles: Exactly 90 degrees
- Obtuse angles: Between 90 and 180 degrees
- Straight angles: Exactly 180 degrees
2. Properties of Angles
Angles that share a vertex have a special relationship:
- Adjacent angles: Two angles that share a common vertex and a common side.
- Vertical angles: Two angles that are opposite each other and share a common vertex.
Properties of vertical angles:
- They are congruent, meaning they have the same measure.
- Their sum is 180 degrees.
Properties of adjacent angles:
- Their sum is less than or equal to 180 degrees.
- If they add up to 180 degrees, they form a straight angle.
3. Measuring Angles
Angles can be measured accurately using a protractor, a tool with a graduated scale.
Steps to measure an angle using a protractor:
- Place the center of the protractor on the vertex of the angle.
- Align the baseline of the protractor with one of the rays.
- Read the angle measurement at the point where the other ray intersects the scale.
Angles can also be measured without a protractor using methods such as:
- Paper folding
- Angle bisectors
- Trigonometric ratios
4. Angle Relationships in Triangles
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
If a triangle has one right angle, it is called a right triangle.
In a right triangle, the Pythagorean theorem relates the lengths of the sides:
a2+ b 2= c 2
where a and b are the lengths of the two shorter sides (legs) and c is the length of the longest side (hypotenuse).
5. Angle Relationships in Parallelograms
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel.
Properties of angles in a parallelogram:
- Opposite angles are congruent.
- Adjacent angles are supplementary, meaning their sum is 180 degrees.
6. Angle Relationships in Circles, Which statement is true about the angles
A central angle is an angle formed by two radii of a circle.
An inscribed angle is an angle formed by two chords of a circle that intersect inside the circle.
Properties of angles in circles:
- The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of the intercepted arc.
- The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of the intercepted arc.
7. Applications of Angles
Angles are used in various real-life applications, including:
- Architecture: Designing buildings and structures
- Engineering: Designing bridges, machines, and other structures
- Navigation: Determining the direction of travel
- Surveying: Measuring distances and angles on land
FAQ Corner: Which Statement Is True About The Angles
What is the definition of an angle?
An angle is a geometric figure formed by two rays or line segments that share a common endpoint, known as the vertex.
What are the different types of angles?
Angles are classified into various types based on their measure: acute angles (less than 90 degrees), right angles (exactly 90 degrees), obtuse angles (between 90 and 180 degrees), and straight angles (exactly 180 degrees).
How do you measure angles?
Angles are typically measured in degrees using a protractor, a specialized tool designed for this purpose. Alternatively, angles can also be measured using trigonometric ratios or geometric relationships.